
The production of Multi-fiber Polarization-Maintaining Fiber assemblies, such as 24F MPO cable assemblies and Multi-fiber Fiber Arrays (FA), involves several critical challenges. These challenges stem from the need to achieve high-precision mechanical alignment, maintain polarization properties, and ensure efficient and reliable mass production. Below is a detailed analysis of the key difficulties involved:
Precision Alignment of Multi-fiber Assemblies
Key Challenges:
Multi-fiber assemblies require precise alignment of multiple fiber end faces to minimize signal loss across all channels. For PM fiber assemblies, in addition to aligning the fiber cores, the fast and slow axes must also be accurately aligned.
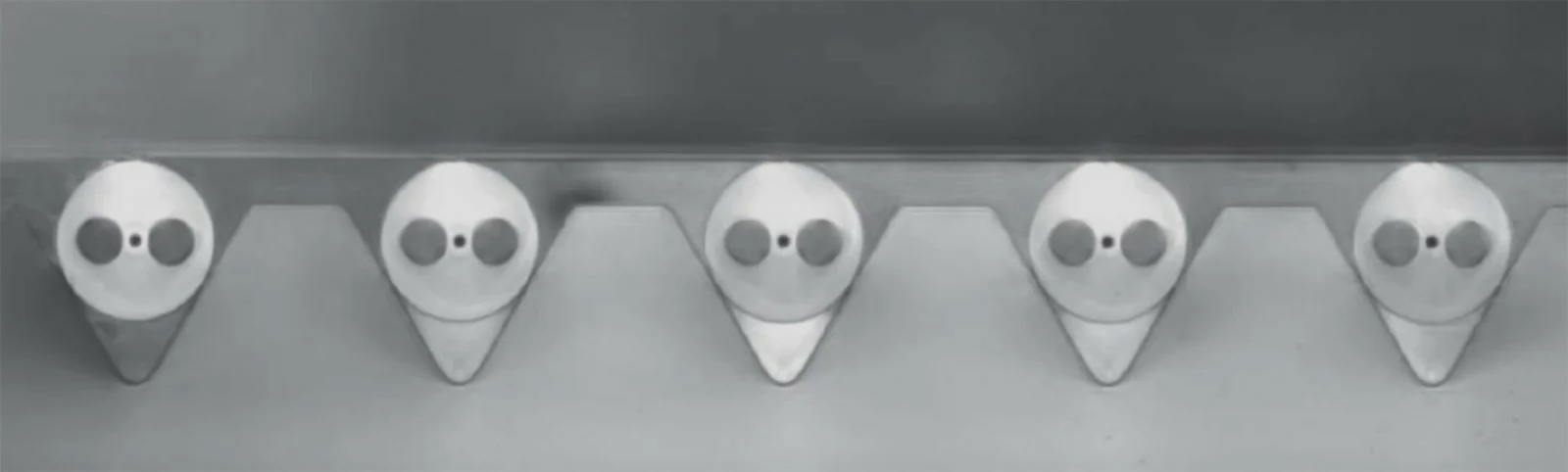
Technical Difficulties:
Core Spacing Accuracy: The core-to-core spacing error must be controlled within sub-micron levels, typically below 0.5 μm.
Axial Misalignment: For PM fiber assemblies, axial alignment error must remain within ±1° to prevent polarization crosstalk.
Preservation of Polarization Properties
Key Challenges:
The primary function of PM fiber assembly is to maintain a specific polarization state. In Multi-fiber connections, it is critical to align the fast and slow axes precisely and avoid disruptions from mechanical stress or temperature variations during assembly and operation.
Technical Difficulties:
High-precision rotational alignment equipment is required to ensure consistent polarization axis orientation for each fiber.
The bonding process (e.g., using UV adhesives or mechanical clamping) must avoid applying lateral stress, which could compromise birefringence.
Temperature fluctuations may induce mechanical stress within the connector, leading to polarization instability.
Complexity of Multi-fiber Design
Key Challenges:
High-density Multi-fiber assemblies, such as 24F MPO cable assemblies, demand intricate designs that balance compactness with optimal optical performance.

Technical Difficulties:
Ferrule Quality: The ferrule must achieve exceptional flatness and surface smoothness, especially for high-density designs involving 24 fibers or more.
Polishing Angle Consistency: Each fiber’s polishing angle must be within ±0.3° to minimize insertion loss and maintain polarization performance.
Thermal and Mechanical Stability: High-density fiber cable assemblies require optimized designs for heat dissipation and structural stability, particularly in high-power optical communication applications.
Challenges in Mass Production
Key Challenges:
Compared to single-core PM fiber cable assemblies, the manufacturing of Multi-fiber product necessitates efficient mass production processes while maintaining high precision and consistency.
Technical Difficulties:
Automation: Many assembly steps still rely on manual operations, making it difficult to achieve both precision and efficiency at scale.
Automated Testing: Specialized equipment is required to rapidly test multi-channel parameters, including optical loss, polarization properties, and axial alignment.
Material Selection: Adhesives and ferrule materials must offer a balance of strength and thermal stability.
Loss and Reliability Control
Key Challenges:
Multi-fiber PM fiber cable assemblies must deliver low insertion loss and high return loss while ensuring long-term reliability.
Technical Difficulties:
Insertion Loss Control: Each fiber channel must have an insertion loss below 0.5 dB (or even lower for certain applications), posing significant challenges in high-channel-count scenarios like 24F.
Environmental Stability: Fiber cable assemblies must maintain consistent performance under varying temperature and humidity conditions.
Mechanical Durability: Fiber cable assemblies must withstand repeated mating cycles, ensuring stable performance after thousands of uses.
Solutions and Technological Trends
1. High-Precision Assembly Equipment:
Advanced fiber alignment and fixation systems incorporating machine vision and nano-scale adjustment technologies can significantly improve assembly accuracy.
2. Automated Polarization Alignment:
Polarization detection systems enable real-time monitoring and adjustment of polarization axis alignment during assembly.
3. High-Performance Materials:
Using low-thermal-expansion and high-strength materials for ferrules and other connector components can minimize the impact of thermal and mechanical stresses on polarization performance.
4. Automated Production Lines:
Developing automated assembly and testing systems for Multi-fiber PM assemblies can ensure high-volume production with consistent quality.
5. Optimized Ferrule Design:
Enhanced ferrule structures, such as floating ferrules, can improve Multi-fiber alignment accuracy and reduce insertion loss.
By addressing these challenges and adopting advanced solutions, the manufacturing of Multi-fiber PM cable assemblies can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and reliability, meeting the stringent requirements of modern optical communication systems.
 Fiber Optic Flex Circuit (FOFC)
Advanced Simulation & Optimization, High Positioning Accuracy, Flexible Customization, Rigorous Reliability Testing
Fiber Optic Flex Circuit (FOFC)
Advanced Simulation & Optimization, High Positioning Accuracy, Flexible Customization, Rigorous Reliability Testing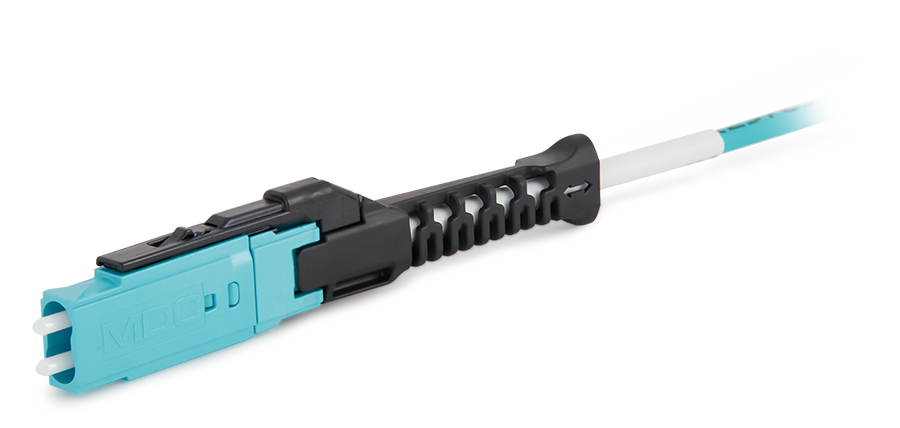 MDC Solution
US Conec's MDC connector is a Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) duplex optical connector, expertly designed for terminating single-mode and multimode fiber cables with diameters up to 2.0mm.
MDC Solution
US Conec's MDC connector is a Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) duplex optical connector, expertly designed for terminating single-mode and multimode fiber cables with diameters up to 2.0mm.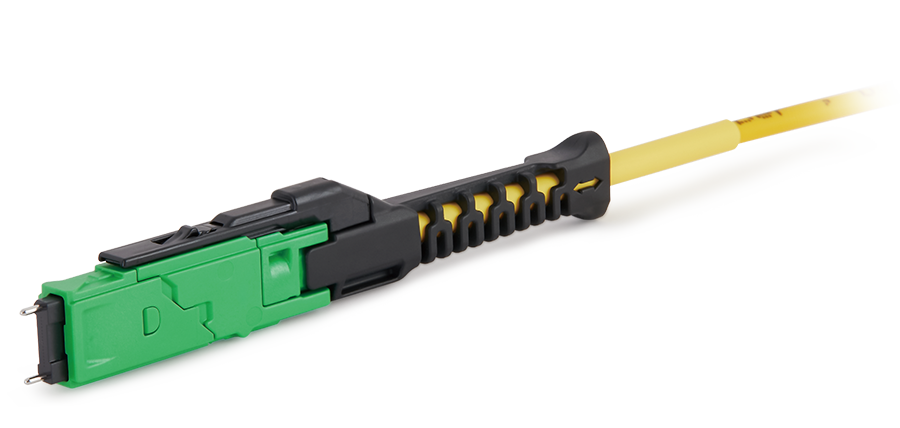 MMC Solution
US Conec's Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) multi-fiber optical connector that redefines high-density connectivity with its cutting-edge TMT ferrule technology and intuitive Direct-Conec™ push-pull boot design.
MMC Solution
US Conec's Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) multi-fiber optical connector that redefines high-density connectivity with its cutting-edge TMT ferrule technology and intuitive Direct-Conec™ push-pull boot design. EN
EN
 jp
jp  fr
fr  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  el
el  nl
nl 







_and_High-Reflection_(HR)_Optical_Coatings.webp)