As businesses scale and embrace digital transformation, the architecture of Data Center Interconnect (DCI) networks becomes crucial in supporting growth, ensuring reliability, and optimizing efficiency. The choice of DCI topology significantly impacts network performance, costs, and disaster recovery capabilities. This article delves into common DCI topologies, their benefits, use cases, and the emerging trends shaping the future of network design.
Overview of DCI Topologies
DCI networks can be designed in various topologies to meet specific operational needs. These designs include point-to-point, ring, mesh, and star architectures, each offering distinct advantages and challenges.
Point-to-Point (P2P) Topology
In a point-to-point setup, direct connections are made between two data centers, ensuring high bandwidth and low-latency communication. This topology is ideal for businesses that need seamless data transfer between two specific locations. However, it's essential to incorporate backup links to mitigate the risk of downtime in case of link failure.
Ring Topology
Ring topologies connect multiple data centers in a circular arrangement, offering bidirectional communication and redundancy. If one link fails, data can be rerouted in the opposite direction, minimizing downtime. This topology is both cost-effective and scalable, making it suitable for regional cloud providers and content delivery networks that require reliable connections without heavy infrastructure costs.
Mesh Topology
In mesh networks, every data center is directly connected to every other one, providing high redundancy and fault tolerance. This setup ensures that data can always be routed through an alternate path in case of failure. Mesh configurations are often used in environments requiring maximum uptime, such as hyperscale cloud services, government institutions, and large financial organizations. However, the complexity and costs associated with this design can be considerable.
Star Topology
Star configurations connect all data centers to a central hub, simplifying network management and reducing overall costs. While this topology is easy to manage, it does present a single point of failure at the hub. This design is most suitable for smaller enterprises or regional service providers that prioritize cost-efficiency and centralized control.
Other DCI topologies, like chain and bus, are also used based on specific business needs:
Chain Topology: Data centers are arranged in a linear sequence, each connected to two others. While it's a cost-effective solution, it offers limited redundancy.
Bus Topology: A single backbone connects all data centers, making it an affordable option for smaller networks, although it may lack the scalability and resilience of other topologies.
Selecting the right topology depends on evaluating factors like redundancy, failover mechanisms, latency requirements, and long-term scalability.
Advantages and Applications of DCI Topologies
Each topology has its unique advantages, making it more suitable for certain industries based on their specific needs for latency, cost, and disaster recovery.
Point-to-point networks are ideal for high-performance environments, such as financial institutions that require fast, low-latency connections for real-time data processing. However, they require additional backup solutions to avoid potential service disruptions.
Mesh networks are designed for environments where maximum uptime is critical. Hyperscalers, cloud service providers, and large enterprises handling mission-critical applications prefer this topology for its fault tolerance and low latency.
When choosing a DCI topology, businesses must consider their specific needs for redundancy, failover capacity, latency, and long-term network scalability.
Emerging Trends in DCI Topology Design
The future of DCI networks is being shaped by several transformative trends that are pushing the boundaries of design and functionality:
AI-Driven Optimization: Artificial intelligence is enhancing DCI networks by enabling dynamic traffic management, predictive maintenance, and automated fault recovery. AI helps optimize performance and minimize downtime through real-time monitoring and traffic analysis.
Open Optical Networks: The rise of open optical networks offers businesses the flexibility to use multi-vendor solutions, which can lead to significant cost savings while avoiding vendor lock-in. This trend allows organizations to achieve customized, cost-efficient network designs.
400G and Beyond: As data demands grow, DCI networks are adopting 400G optical network technologies to support higher bandwidth and lower latency. These advancements are essential for enterprises dealing with large-scale data applications like AI, big data analytics, and cloud services.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN is revolutionizing DCI by allowing greater network agility and automation. With SDN, organizations can allocate bandwidth, create virtual networks, and respond to traffic changes without manual intervention, reducing operational complexity and costs.
Conclusion
Selecting the right DCI topology is crucial to ensuring a data center network is resilient, scalable, and cost-efficient. Whether prioritizing low-latency connections, redundancy, or centralized management, T&S offers flexible and high-performance DCI solutions tailored to the dynamic needs of today's businesses. Our range of DCI products supports a variety of topologies, providing organizations with the flexibility to choose the architecture that best fits their specific requirements. As new technologies emerge, businesses can leverage these innovations to future-proof their DCI infrastructure, keeping pace with the ever-evolving demands of the digital era.
 Fiber Optic Flex Circuit (FOFC)
Advanced Simulation & Optimization, High Positioning Accuracy, Flexible Customization, Rigorous Reliability Testing
Fiber Optic Flex Circuit (FOFC)
Advanced Simulation & Optimization, High Positioning Accuracy, Flexible Customization, Rigorous Reliability Testing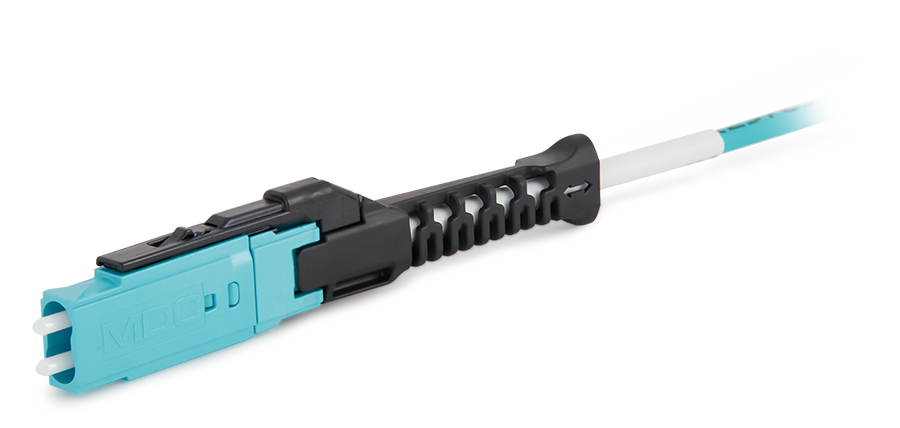 MDC Solution
US Conec's MDC connector is a Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) duplex optical connector, expertly designed for terminating single-mode and multimode fiber cables with diameters up to 2.0mm.
MDC Solution
US Conec's MDC connector is a Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) duplex optical connector, expertly designed for terminating single-mode and multimode fiber cables with diameters up to 2.0mm.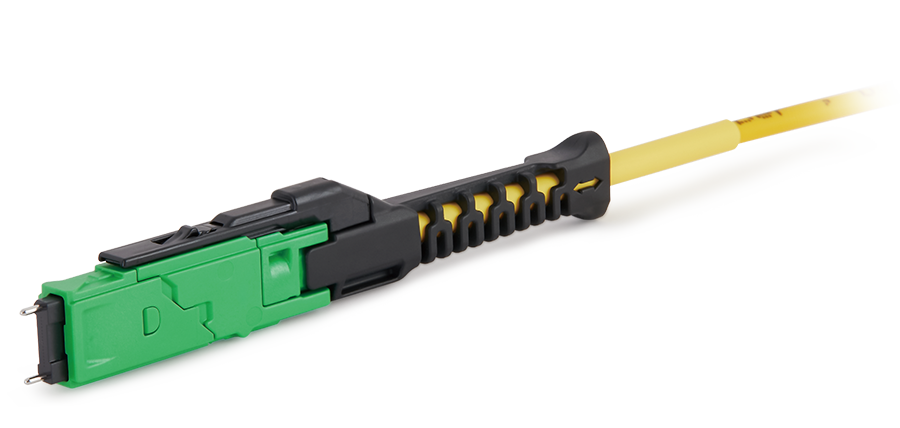 MMC Solution
US Conec's Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) multi-fiber optical connector that redefines high-density connectivity with its cutting-edge TMT ferrule technology and intuitive Direct-Conec™ push-pull boot design.
MMC Solution
US Conec's Very Small Form Factor (VSFF) multi-fiber optical connector that redefines high-density connectivity with its cutting-edge TMT ferrule technology and intuitive Direct-Conec™ push-pull boot design. EN
EN
 jp
jp  fr
fr  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  el
el  nl
nl 





_and_High-Reflection_(HR)_Optical_Coatings.webp)